What Is Cloud Architecture? Components and How It Works in Detail
Nov 10, 2025Cloud architecture is the foundation of modern technology services, enabling businesses and individuals to optimize data storage, processing, and service delivery over the internet in a flexible and cost-efficient manner. Let’s explore this concept in depth with Vcloudia.
What is Cloud Architecture?
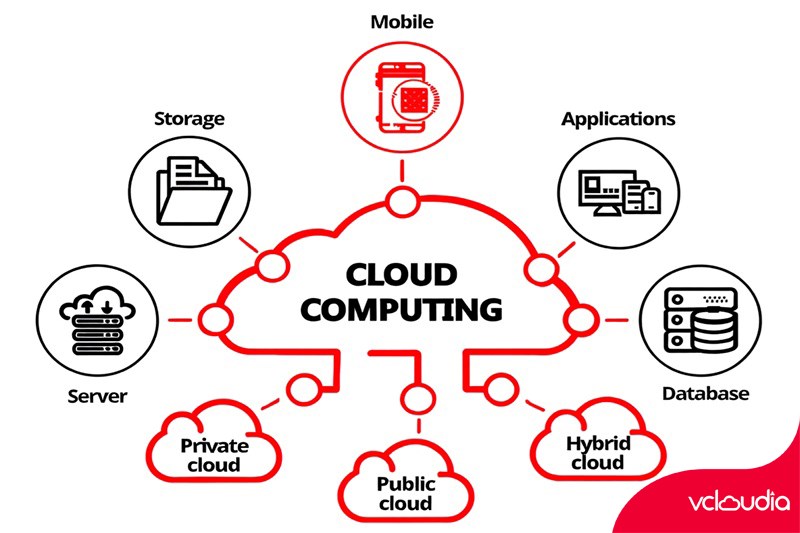
Cloud architecture refers to the organization, design, and coordination of technical components such as hardware, software, and networking systems to deliver computing services over the internet with scalability, flexibility, and security.
Unlike traditional IT systems, cloud architecture goes beyond simple data storage — it also encompasses data processing, distribution, and efficient resource management to ensure continuous operation.
These architectural models allow businesses to deploy services faster, reduce upfront investment risks, and easily scale up or down according to market demands — fostering competitiveness and innovation.
Key Components of Cloud Architecture
Cloud architecture is not a single system but a collection of interconnected components that work together to deliver seamless, multidimensional cloud services. Each component performs specific functions, contributing to the system’s overall efficiency and user experience.
The cloud architecture can be divided into four main layers: front-end, back-end, networking, and service models, along with management and security. Understanding these components helps developers, system administrators, and enterprises make informed decisions when designing a suitable cloud infrastructure.
1. Front-End
The front-end is the user interface where clients and businesses interact directly with the cloud system. It includes web applications, mobile apps, and any online platforms that rely on cloud-based services.
Effective front-end design must ensure usability, flexibility, and scalability across different devices and browsers. Security measures such as protection against SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS) are also critical.
Modern frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js have become increasingly popular for building dynamic and efficient cloud-based interfaces.
The front-end connects directly with the back-end or through the network layer, ensuring a smooth and responsive user experience — a key factor in enhancing customer satisfaction and business performance.
2. Back-End
The back-end is the core engine of cloud architecture. It handles data processing, business logic, and other complex operations. It consists of APIs, processing servers, data management systems, and other essential services that keep the entire infrastructure running.
In cloud systems, the back-end also integrates data from multiple sources, processes user requests from the front-end, and delivers the results. Popular frameworks like Node.js, Django, and Spring Boot are widely used to develop scalable and flexible back-end systems.
Additionally, the back-end is responsible for implementing security protocols, user authentication, access control, and resource management. Regular updates and optimization enhance both performance and system security — crucial for maintaining a modern, reliable cloud environment.
3. Networking
The networking layer interconnects all cloud architecture components through data transmission protocols, ensuring information flows securely, accurately, and quickly. It acts as the backbone of cloud operations.
Networking in cloud environments extends beyond simple cables or Wi-Fi. It includes advanced technologies such as VPNs, Software-Defined Networking (SDN), and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) that enhance global data delivery speed and reduce latency, improving user experience.
Robust network infrastructure also involves implementing data encryption, network access control, and intelligent firewalls — all of which are essential for ensuring reliability, security, and system integrity.
4. Service Models
Service models form the core of cloud architecture, defining how resources and services are provided to users. The three most common models are:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides infrastructure resources such as servers, storage, and networking as services. It offers high flexibility and control, making it suitable for enterprises that need customized environments.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a development platform where developers can build, test, and deploy applications without managing underlying infrastructure. It accelerates development and collaboration.
Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers ready-to-use software over the internet — such as email, CRM, project management, or collaboration tools — ideal for organizations seeking cost-effective, low-maintenance solutions.
5. Management and Security
Management and security are the cornerstones of successful cloud architecture. Management involves resource monitoring, performance tracking, and automation to ensure scalability and operational efficiency.
Security remains a top priority. Technologies such as data encryption, identity authentication, access control, and intrusion prevention systems protect sensitive information from cyberattacks.
International compliance standards like ISO and GDPR should be integrated to establish a trustworthy and secure infrastructure.
Tools such as Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) help automatically detect vulnerabilities and recommend corrective measures. Organizations should also implement clear policies, train employees in cybersecurity awareness, and continually adopt new defense technologies.
How Cloud Architecture works?
In operation, cloud architecture integrates all its components to deliver seamless, secure, and efficient services. The process begins when a user sends a request through the front-end. The back-end processes the data, and the networking layer ensures smooth communication between systems.
The management and security layers oversee and control activities, identifying potential risks or technical issues in real time.
Modern cloud environments often incorporate automation, orchestration, and containerization technologies such as Docker and Kubernetes, allowing systems to scale dynamically based on demand.
Additionally, cloud systems use Big Data analytics and predictive algorithms to allocate resources intelligently, minimizing downtime, optimizing costs, and enhancing the end-user experience.
Benefits of Cloud Architecture
Cloud architecture offers numerous advantages that contribute to business success in the digital age:
- Scalability: Easily adjust resources according to market demand, avoiding over- or under-investment.
- Operational Flexibility: Launch new services, test products, and expand markets quickly without heavy infrastructure costs.
- Cost Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go models reduce initial investment and optimize long-term budgets.
- Enhanced Security and Resilience: Strong backup and disaster recovery capabilities ensure continuous service availability.
- Global Accessibility: Access systems and data anytime, anywhere — ideal for multinational operations.
Principles of Building Cloud Architecture
To develop an effective cloud system, several core principles must be followed:
- Scalability and Flexibility: Ensure the architecture adapts easily to organizational and market changes.
- Security First: Focus on data protection, access control, and risk reduction.
- Performance Optimization: Maintain smooth, uninterrupted service delivery.
- Standards Compliance: Align with international regulations and best practices for reliability and legality.
- Adhering to these principles builds a robust, sustainable cloud architecture that supports long-term growth.
Real-World Applications of Cloud Architecture
Cloud architecture is now widely used across industries — from businesses and governments to public services. Major providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure rely on this architecture to deliver fast, secure, and scalable global services.
In e-commerce, platforms like Shopee, Lazada, and Tiki use cloud architecture to handle millions of daily transactions, especially during peak seasons, ensuring stable performance and seamless user experiences.
Beyond commerce, sectors such as healthcare, education, banking, and government use cloud architecture for data management, digital service delivery, and online collaboration — reducing costs and improving operational agility while maintaining data security.
Conclusion
Cloud architecture is more than just technology — it is a strategic framework for growth in the digital age. With well-defined components, operational principles, and modern design, it delivers exceptional advantages in scalability, security, performance, and cost efficiency.
As technology continues to evolve, cloud architecture will remain at the heart of business innovation and digital transformation. Understanding how it works empowers organizations and individuals to harness its full potential — achieving sustainable success in the modern digital landscape.
Looking for a high-performance, secure solution?
Explore the services offered by Vcloudia – a leading provider of cloud computing and data center solutions. Contact us for expert consultation and find the right model for your needs:
- Hotline: +855 888 55 66 08 (free of charge)
- Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/vcloudia/
- Website: https://vcloudia.com
Related news
What Is FaaS? Everything You Need to Know About Function-as-a-Service
In a world where technology is constantly evolving and shifting at high speed, FaaS has become an important concept, opening up new opportunities for developers and businesses to optimize application performance. In this article, vCloudia helps you understand what FaaS is, how it works, its benefits, and its practical applications.
What Is SaaS? Everything You Need to Know About Software-as-a-Service
SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) has become a crucial component of the global digital transformation trend, offering numerous advantages over traditional software models. In this article, let’s explore with vCloudia the concepts, roles, operating mechanisms, and future trends of the SaaS model.
What Is a Cloud Firewall? Why It Is Essential and Important
In today’s technology-driven world—where data and online services are expanding at an unprecedented pace—Cloud Firewalls have become an indispensable component of enterprise cybersecurity strategies.
Can Cloud Data Be Synchronized To A Server?
In today’s digital age, synchronizing cloud data with servers has become an essential component of data management for businesses and organizations. This combination enhances flexibility, security, and data accessibility anytime, anywhere—thereby boosting operational efficiency and fostering innovation.
What Is PaaS? Key Insights into Platform as a Service
In today’s rapidly evolving digital era, both businesses and developers are seeking optimal solutions to build software quickly, efficiently, and cost-effectively. One of the most prominent solutions is PaaS – Platform as a Service. Let’s explore it in detail with Vcloudia in the following article.
What is IaaS? Everything You Need to Know About Infrastructure as a Service
IaaS, short for Infrastructure as a Service, is one of the most widely used cloud computing models today. It offers businesses numerous benefits in terms of flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. This article will help you better understand what IaaS is, its key components, advantages, disadvantages, and real-world applications.
Cloud Server vs Dedicated Server: What Are the Differences?
In this article, we will take a deep dive into a detailed comparison between Cloud Servers and Dedicated Servers to help you make the most accurate and optimal choice for your business or project. Let’s explore this topic with Vcloudia right now.
How To Build Your Own Cloud Server?
In this article, Vcloudia will provide a detailed, step-by-step guide on how you can build your own cloud server—from the initial preparation stages and choosing the right deployment model, to common errors and how to fix them.
What Is Multi Cloud? How It Works, Along With Its Advantages and Disadvantages
In today’s digital era, businesses are constantly seeking optimal solutions to enhance operational efficiency, minimize risks, and maximize profitability. One increasingly popular strategy is Multi Cloud. In this article, Vcloudia explores Multi Cloud in depth — from theory to real-world applications.
